| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- FSE
- ECG gating
- wrap around artifact
- MR angiography
- saturation band
- T2강조영상
- MRA
- fast spin echo
- T2 이완
- T2WI
- T1강조영상
- no phase wrap
- chemical shift artifact
- 자기공명혈관조영술
- saturation pulse
- K-space
- 방사선사나라
- MRI gantry
- MRI 영상변수
- 사전포화펄스
- T1WI
- receive bandwidth
- tof
- fractional echo
- 동위상 탈위상
- TR TE
- MRI image parameters
- radiographer nara
- aliasing artifact
- slice gap
- Today
- Total
방사선사나라 Radiographer Nara
[MRI](영/한) Gradient Pulse / 그라디언트 펄스 본문
(영어/영문/English)
1. Slice selection gradient
To select an image slice, an RF pulse having a frequency range corresponding to a desired slice thickness is applied while a gradient is applied. At this time, the applied gradient is called the slice selection gradient (Gs).
Since the phase of the spins is scattered and the signal becomes small while the gradient is applied, after the RF pulse is applied, a compensating gradient (rephase gradient, Gs) with opposite polarity should be applied to maximize the signal.

2. Phase encoding gradient
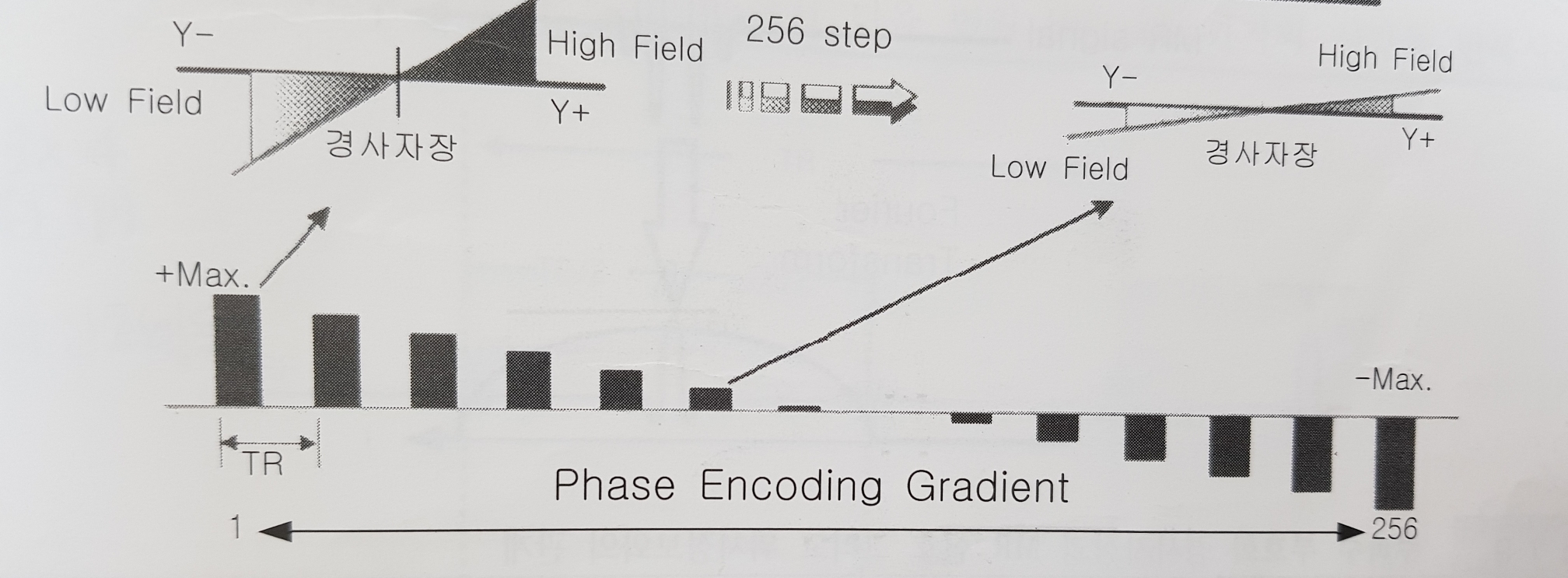
After the slice of the image is selected, it is necessary to grasp the location information for each pixel in one slice. For this, an gradient is applied to one axis (Y-axis) of the slice. This gradient is called a phase encoding gradient.(Gp)
The magnitude of the gradient determines the magnitude of the signal. If the magnitude of the gradient is large, the spins are dephased so that the signal is small, but contains a lot of information about the position.
If the phase encoding gradient step is 256, a different magnitude of the gradient is applied each time during 256 TR. And the 128th gradient is the smallest, so the signal at this time is the largest. In addition, 1st and 256th, 2nd and 255th, 3rd and 254th ... are the same size and the direction of polarity is opposite, so the signal size is the same and the phase is opposite.
3. Frequency encoding gradient (Readout gradient)
The position information must also be known for the X, and the applied gradient is the frequency encoding gradient.(Gr)
Like a phase encoding gradient, a gradient is applied to dephase the spins for each pixel. The gradient of opposite polarity is applied to rephase the spins and that time we can get signal.
when a signal is read while the gradient is applied, it is called a readout gradient. And it is also called a frequency encoding gradient because the location information is frequency encoded by the gradient.
by radiographer nara
(국어/국문/Korean)
1. 단면선택 경사자장
영상단면의 선택을 위해서는 경사자장을 가한 상태에서 원하는 단면의 두께에 해당하는 주파수범위를 갖는 RF 펄스를 가해준다. 이때 인가되는 경사자장을 단면선택 경사자장이라고 한다.
경사자장이 가해지는 동안에는 스핀들의 위상이 흩어져 신호가 작아지기 때문에 RF 펄스가 가해진 이후에 극성이 반대인 보상 경사자계를 가하여 신호가 최대가 되도록 해야한다.
2. 위상 부호화 경사자장
영상의 단면이 선택된 다음에는 한 단면 안에서의 각각의 화소에 대한 위치정보를 파악해야한다. 이를 위하여 단면의 한쪽 축(Y축)으로 경사자장이 인가되는데 이 경사자장을 위상 부호화 경사자장이라고 한다.
인가되는 경사자장의 크기가 신호의 크기를 좌우하는데 경사자장의 크기가 클 경우에는 스핀들의 위상이 많이 흩어져 신호가 작지만 위치에 대한 정보를 많이 포함한다.
위상부호화수가 256이라면 256번의 TR 동안 매번 다른 크기의 경사자장이 인가되고 128번째의 경사자장의 크기가 가장 작기 때문에 이때의 신호가 가장 크다. 또한 1번과 256번, 2번과 255번, 3번과 254번 ... 은 크기가 같고 극성의 방향이 반대이므로 신호의 크기는 같고 그 위상은 반대가 된다.
3. 주파수 부호화 경사자장
X축에 대해서도 위치정보를 알아야 하는데 이때 인가되는 경사자장이 주파수 부호화 경사자장이다.
위상 부호화 경사자장처럼 경사자장을 인가하여 각 화소마다 스핀들을 탈위상 시킨다. 극성이 반대인 자계를 인가하여 스핀들을 재위상화시키는데 이때 신호를 받는다.
자장이 걸린 상태에서 신호를 읽는다고 해서 판독경사자장이라고 하고 경사자장에 의해 위치정보가 주파수 부호화된다고 하여 주파수 부호화 경사자장이라고도 한다.
- 방사선사나라
'자기공명영상 (MRI)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [MRI] Gradient Echo (GRE) / 경사자계 에코 신호 (0) | 2020.04.20 |
|---|---|
| [MRI] (영/한) Spin Echo (SE) / 스핀에코 (0) | 2020.04.19 |
| [MRI](영/한) T2 decay, T2* relaxation, Gradient dephase / T2 붕괴, T2* 이완, 경사자장 탈위상화 (0) | 2020.04.16 |
| [MRI] (영/한) Image parameter(6) - FC , Gating / 영상변수(6) - 유동보정, 게이팅 (0) | 2020.04.14 |
| [MRI] (영/한) Image parameter(5) - Bandwidth , Saturation Pulse / 영상변수(5) - 주파수폭, 포화펄스 (0) | 2020.04.13 |