| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- T2WI
- tof
- slice gap
- 사전포화펄스
- fractional echo
- 동위상 탈위상
- receive bandwidth
- T2강조영상
- TR TE
- T1WI
- MRA
- aliasing artifact
- MRI image parameters
- saturation band
- radiographer nara
- 자기공명혈관조영술
- MRI 영상변수
- T2 이완
- fast spin echo
- no phase wrap
- chemical shift artifact
- FSE
- saturation pulse
- 방사선사나라
- MRI gantry
- K-space
- MR angiography
- wrap around artifact
- T1강조영상
- ECG gating
- Today
- Total
방사선사나라 Radiographer Nara
[MRI] (영/한) chemical shift artifact/ 화학적 이동 인공물 본문
(영어/영문/English)
Chemical shift artifact?
The chemical structure of fat and water is different, and the difference in precession frequency is proportional to the intensity of the main magnetic field.
Fat and water have a chemical shift of 3.5 part per million (ppm) and fat resonates at a lower frequency than water.
At a frequency of 0.5 Tesla, it resonates at a frequency with a difference of 74 Hertz, 1.0 Tesla, 147 Hertz, and 1.5 Tesla, 244 Hertz.
Also, the smaller the receive bandwidth, the more pixels are moved and the more artifacts are created.
It moves about 1 pixel at ± 32 kHz, about 1.7 pixels at ± 16 kHz, and about 3 pixels at ± 8 kHz.
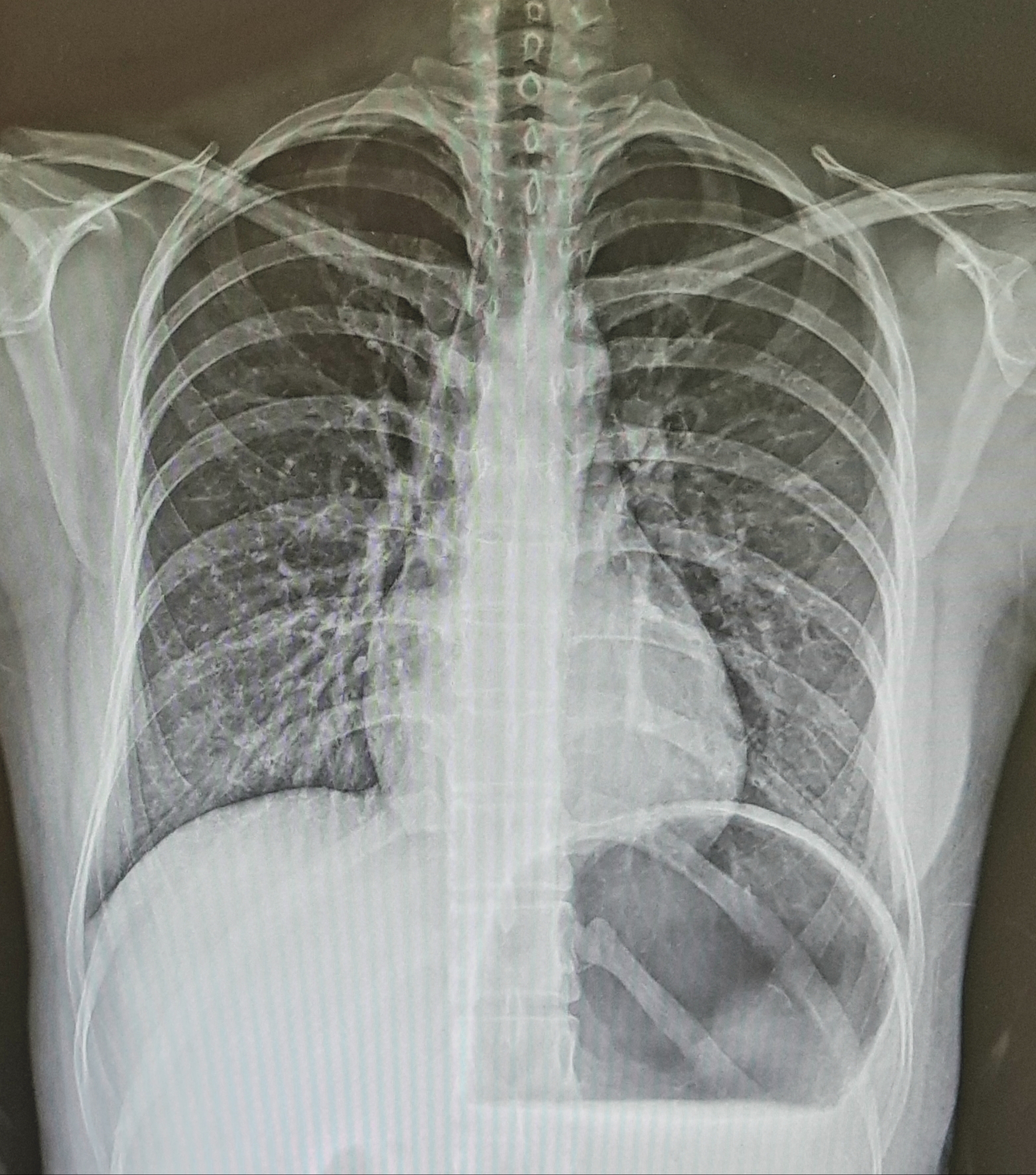
This chemical shift artifact appears as signal void and signal enhancement, and fat moves in the lower frequency direction giving a strong signal at lower frequency and darker at the higher frequency.
It usually occurs in eyeball or kidney images and occurs in the frequency direction.
Prevention
The artifact can be reduced by increasing the receive bandwidth or by using equipment with a low intensity main magnetic field.
(However, there is a disadvantage that SNR decreases when the receive bandwidth is increased.)
Alternatively, a method of suppressing fat signals using a fat suppression technique is used.


by radiographer nara
(국어/국문/Korean)
화학적 이동 인공물?
지방과 물의 화학적 환경이 다른데서 기인하며 세차주파수의 차이는 주 자장의 강도에 비례한다.
지방과 물은 3.5ppm(part per million)의 화학적 이동을 가지고 있고 지방이 물보다 낮은 주파수에서 공명하게 된다.
0.5테슬라의 자장에서는 74헤르츠, 1.0 테슬라의 자장에서는 147헤르츠, 1.5테슬라의 자장에서는 244헤르츠만큼의 차이가 있는 주파수에서 공명하게 된다.
또 수신대역폭이 작을수록 픽셀의 이동이 많고 이동이 많으면 더 많은 인공물이 생긴다.
±32kHz에선 약 1픽셀 이동, ±16kHz에선 약 1.7픽셀 이동, ±8kHz에선 약 3픽셀이 이동한다.
이 화학적 이동 인공물은 신호감소와 신호증강으로 나타나며 지방은 낮은 주파수 방향으로 이동하여 강한 신호를 내고 높은 주파수 쪽은 어둡게 나타난다.
보통 안구나 신장 영상에서 많이 발생하며 주파수 방향으로 생긴다.
방지법
수신대역폭을 증가하거나, 낮은 강도의 주 자장의 장비를 사용하는 방법으로 인공물을 감소 시킬 수 있다.
(다만 수신대역폭을 증가시키면 SNR이 감소한다는 단점이 있다.)
혹은 지방소거 기법을 사용하여 지방신호를 억제하는 방법을 사용한다.
- 방사선사 나라
'자기공명영상 (MRI)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [MRI] (영/한) Zipper artifact / 지퍼 인공물 (0) | 2020.05.11 |
|---|---|
| [MRI] (영/한) Magnetic susceptibility artifact / 자화 감수성 인공물 (0) | 2020.05.10 |
| [MRI] (영/한) Wrap around (aliasing) artifact / 엘리어싱 인공물 (0) | 2020.05.07 |
| [MRI] (영/한) Phase mismapping artifact / 위상의 미스맵핑 인공물 (0) | 2020.05.06 |
| [MRI] (영/한) SENSE (Sensitivity - Encoded) / 센스기법 (0) | 2020.05.02 |